This post is dedicated to explaining CCNA math. It constitutes Issue 5 of my CCNA 200-301 study notes.
For a more comprehensive CCNA math resource: CCNA math portal.
- The meaning of base 2, 10, and 16 number systems
- Decimal to binary conversion
- Binary to decimal conversion
- Hexadecimal to decimal conversion
- Decimal to hexadecimal conversion
- Key references
You may also be interested in CCNA 200-301 study notes.
The meaning of base 2, 10, and 16 number systems
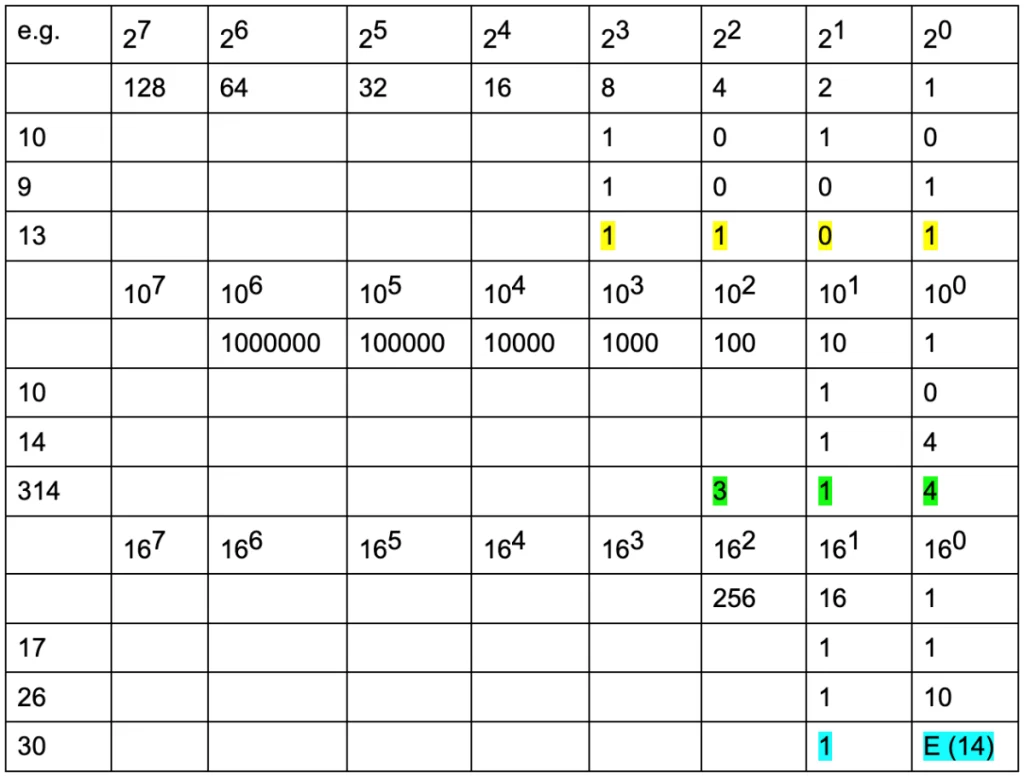
*How the binary system works: 0, 1
Example 1: 10 is 1 value of 8 and 0 value of 4 and 1 value of 2 and 0 value of 1 =1010
Example 2: 9 = 1×8 + 0x4 + 0x2 + 1×1 = 1001
Example 3: 13 = 1×8 + 1×4 +0x2 +1×1 = 1101
*How the decimal system works: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Example 1: 10 is 1 value of 10 and 0 value of 1
Example 2: 14 is 1 value of 10 and 4 values of 1 = 1×10 + 4×1
Example 3: 314 = 3×100 + 1×10 + 4×1
*How the hexadecimal system works: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
Example 1: 17 = 1×16 + 1×1 = 11
Example 2: 26 = 1 value of 16 and 10 values of 1 = 1×16 + 10×1 = 1A
Example 3: 30 = 1×16 + 14×1 = 1E
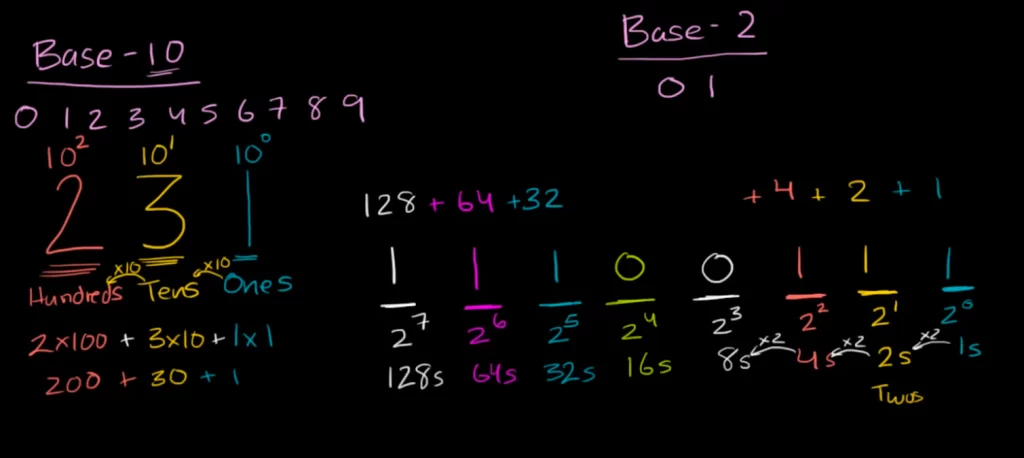
Decimal to binary conversion
Example 1: convert 221 to binary.
221 – 128 = 93
Now,
93 – 64 = 29
29 – 16 = 13
13 – 8 = 5
5 – 4 = 1
1-1 = 0
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
221 equals 11011101.
Example 2: convert the following IPv4 address to binary format.
IPv4 address: 192.168.1.254.
An IPv4 address is a series of 32 bits (4 bytes) split up into four octets then written in dotted decimal format.
We want to write each octet value in binary numbers. Following the previous examples:
| Decimal | 192 | 168 | 1 | 254 |
| Binary | 11000000 | 10101000 | 00000001 | 11111110 |
Binary to decimal conversion
Example: 10001111 equals 143. But how come?
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
1×128 + 1×8 +1×4 +1×2 + 1×1 = 128 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 143.
Hexadecimal to decimal conversion
CDE in hexadecimal = 3294 in decimal. But how come?
| 167 | 166 | 165 | 164 | 163 | 162 | 161 | 160 |
| 4096 | 256 | 16 | 1 | ||||
| C (12) | D (13) | E (14) |
CDE = 12×256 + 13×16 + 14×1 = 3072 + 208 + 14 = 3294.
Decimal to hexadecimal conversion
Convert 3294 to hexadecimal numbers.
3294/256 = 12.867
3294 – 12×256 = 222
Now,
222/16 = 13.875
222 – 13×16 = 14
Finally,
14/1 = 14
14 – 14×1 = 0
3294 = 12×256 + 13×16 + 14×1 = CDE
Key references
Hexadecimal number system | Applying mathematical reasoning | Pre-Algebra | Khan Academy
Related content
Classless IPv4 addressing and subnetting
Compliance frameworks and industry standards
How data flow through the Internet
How to break into information security
IT career paths – everything you need to know
Job roles in IT and cybersecurity
Network security risk mitigation best practices
The GRC approach to managing cybersecurity
The penetration testing process
The Security Operations Center (SOC) career path
Back to DTI Courses